Although routine eye matters can frequently be handled by a general veterinarian, sometimes the problems may be serious and require special attention. These include:
- Cataracts
- Corneal ulcer
- Entropion
- Glaucoma
- Prolapsed gland of the nictitans (cherry eye)
- Uveitis
Moreover, it is a very sensitive organ, the function of which may be affected even with mild insult to its homeostasis, due to direct injury or due to other local or systemic diseases. And because the ocular tissues are extremely sensitive, even the simple goal of ophthalmology to getting the right therapeutic dose to the target ocular tissue by a method that does not damage healthy tissue becomes more challenging.
- Squinting or holding eye(s) shut
- Scratching or rubbing at eye(s)
- Excessive green or yellow discharge
- Swelling of the eye(s) or eyelid(s)
- A change in color, especially cloudiness or redness
- Runs into unfamiliar objects
- Difficulty finding familiar objects (like water bowls, toys, etc.)
- Suddenly unwilling to jump or climb
- Lethargy, confusion, weakness, anxiety, depression
- Unable to locate moving or stationary objects
- Refusal to move in darkness
- Develops aggressive behavior
- Seeks security (tries to remain close to your feet more than usual)
- Exaggerated “high-stepping” gait
- Keeps head down (constantly sniffs the ground while walking)
Steps in examination and diagnosis include:
- Vision testing: Menace response (a conditioned avoidance response response ending with a blink), cotton ball tracking, maze testing
- Gross evaluation of the head: Symmetry of the two sides of the face, comparison of palpebral fissures for their size, symmetry, position of the upper eyelid cilia and the general eyelid form, as well as characterization of any ocular discharge (serous, mucoid, mucopurulent, or serosanguinous)
- Pupillary symmetry
- Reflexes and neurological responses: Palpebral reflex, corneal reflex, dazzle reflex, and pupillary light reflex
- Palpation: Hard or soft, movable or fixed, sensitive or insensitive and orbital or extra-orbital swellings/masses
- Mouth examination
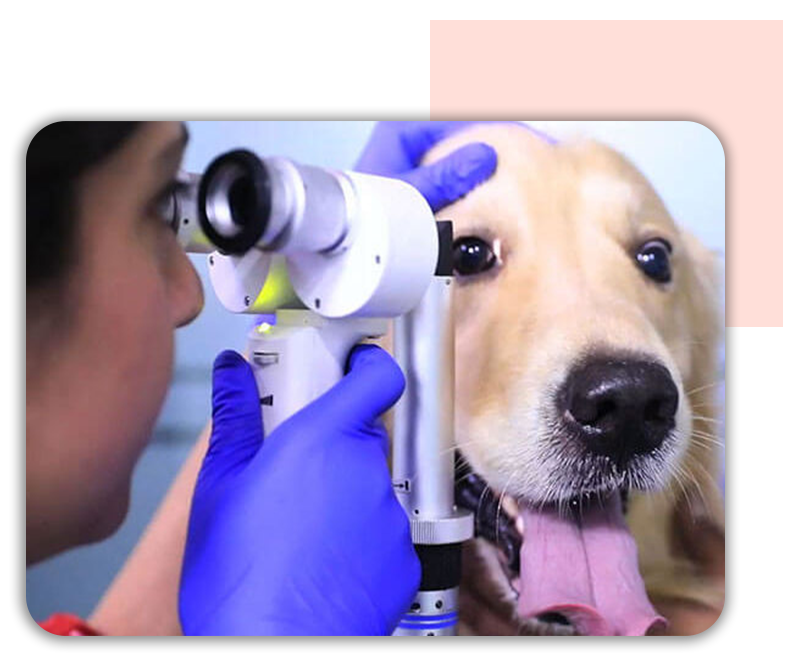
- Close gross examination: Eyelids, conjunctiva, third eyelid, cornea, anterior chamber, iris, lens, vitreous and fundus (direct and indirect ophthalmoscopic exam), slit lamp examinations
- Special diagnostic tests if required: Schirmer tear test, culture, fluorescein, eyelid eversion, nasolacrimal flush, tonometry, conjunctival scraping, gonioscopy, ocular ultrasound, electroretinogram
At MaxVets, we have a fully equipped ophthalmology unit with all diagnostic and surgical equipment. We routinely perform corneal and intraoccular surgical procedures such conjunctival grafts and cataract phacoemulsification procedures.
- Eye surgeries are performed to correct debilitating diseases like glaucoma, cataracts, dry eye, and corneal ulcers.
- Other procedures are also performed for achieving the following goals:
- Protect corneas affected by laceration or ulceration
- Remove cataracts or eyelid masses
Correct congenital eyelid abnormalities.
Meet our team members











